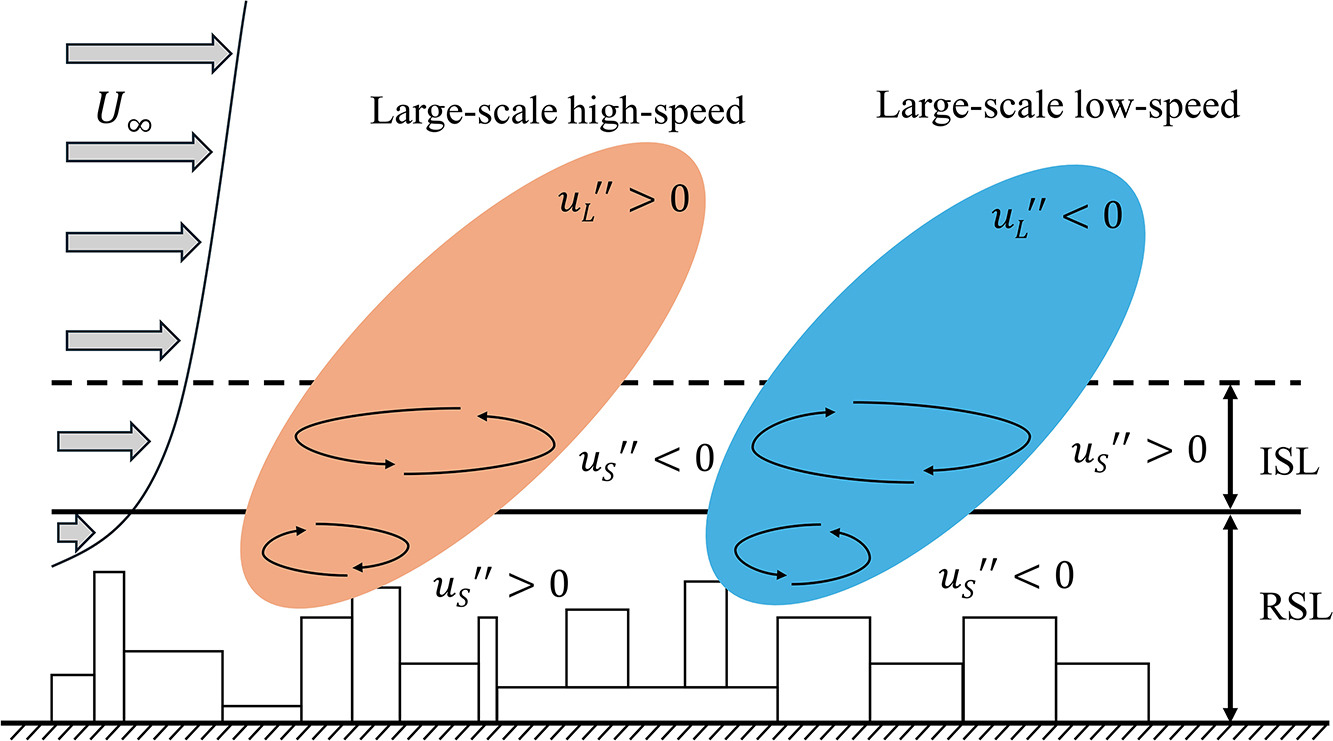
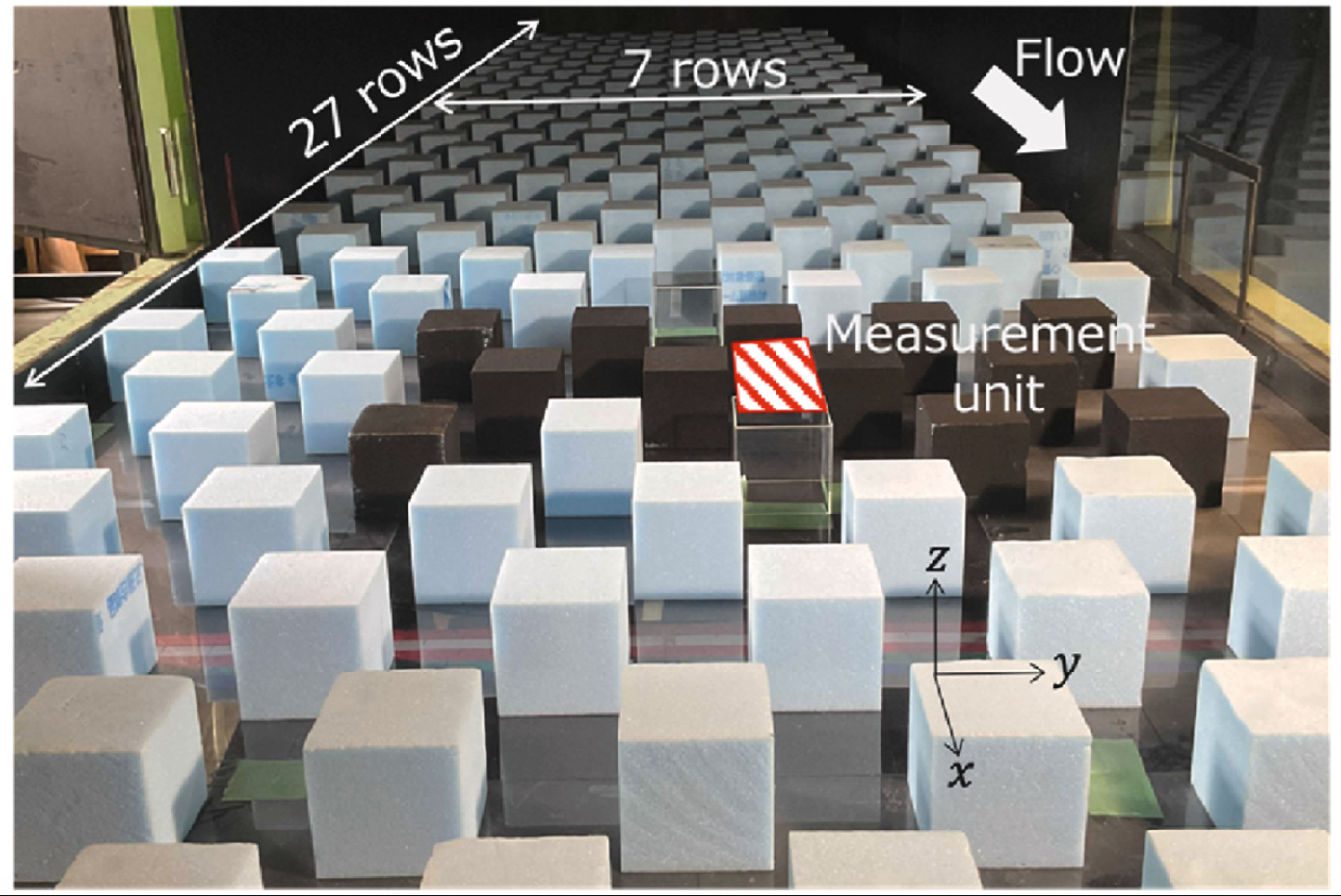
I will serve as co-chair for the Object Detection session at IROS 2024.
October 2024

I will attend IROS 2024 in Abu Dhabi, UAE.
October 2024

I will be the GTA for CSE 4360 (Robotics) course this semester!
August 2024

V3D-SLAM and Refined PanMap papers are accepted at IROS 2024!
June 2024

I will continue my PhD studies in robotics at the LEARN Lab.
May 2024

I finished my undergrad studies in computer science at UTA.
May 2024

I will attend IROS 2023 in Detroit, Michigan.
October 2023

I will present at ISR 2023 in Stuttgart, Germany.
September 2023

The deformable object classification paper is accepted at ISR 2023!
June 2023

The multiplanar self-calibration paper is accepted at IROS 2023!
June 2023
My thesis proposal is approved by the Honors College!
June 2023

I am invited to review papers at CASE 2023.
April 2023

The PerFC paper is accepted at FLAIRS-36!
March 2023

I am invited to review papers at UR 2023.
February 2023
Spidey won sponsorship prizes at HackMIT 2022!
October 2022

I joined the Learning and Adaptive Robotics (LEARN) Lab at UTA.
August 2022

The IoTree paper is accepted at MobiCom 2022!
June 2022

iPlanter won prizes at GaTech RoboTech Hackathon 2022!
April 2022

I joined the Wireless and Sensor Systems Lab (WSSL) at UTA.
August 2021

I start my undergrad at the University of Texas at Arlington (UTA).
August 2020